International Demonstration Teaching Team
for the Course of Analog and Digital Signal Processing
一、课程简介
Introduction
《模拟与数字信号处理》(Analog and Digital Signal Processing)是西里西亚智能科学与工程学院自动化专业本科三年级学生的一门专业必修课程。本课程于秋季学期开设,总计48学时,3.0学分,采用全英文教学模式。课程由波兰西里西亚技术大学与燕山大学信息科学与工程学院和电气工程学院中外双方教师联合授课。该课程旨在让学生了解信号与系统表示的各种方法,熟悉模拟与数字信号处理的基本原理和方法。课程理论和实验教学相结合,不仅注重夯实学生在信号、系统、变换域分析等方面的理论基础,更通过配套的实验环节深化对基本概念、方法与原理的理解与应用。本课程培养学生的工程思维、实践能力与创新意识,为其在自动化及相关领域解决复杂工程问题、从事更高层次的学习与研究奠定基础,对达成专业培养目标起到重要的支撑作用。
Analog and Digital Signal Processing is a compulsory course for third-year undergraduate students majoring in Automation of the Silesian College of Intelligent Science and Engineering at Yanshan University. The course is offered in the autumn semester, with a total of 48 teaching hours and 3.0 credits and is delivered entirely in English. It is jointly taught by faculty from the Silesian University of Technology in Poland and the School of Information Science & Engineering and the School of Electrical Engineering of Yanshan University in China.
The course aims to enable students to understand various methods of signal and system representation, and to familiarize them with the fundamental principles and techniques of analog and digital signal processing. The course combines theoretical lectures with laboratory instruction, not only strengthening students' theoretical foundation in signals, systems, and transform domain analysis but also deepening their understanding and application of basic concepts, methods, and principles through supporting laboratory sessions. It cultivates students' engineering thinking, practical ability, and innovative awareness, laying a solid foundation for solving complex engineering problems in automation and related fields and pursuing further studies and research. The course plays a critical supporting role in achieving the program's educational objectives.
二、团队成员
Team Members
KatarzynaMoscinska,博士,教授,担任《模拟与数字信号处理》课程的外方负责教师。现就职于西里西亚技术大学自动控制、电子与计算机科学学院,教学副院长。Moscinska教授拥有丰富的教学经验,她讲授的课程包括神经网络、电工学基础、信号处理基础、数字信号处理、电子电路的计算机分析、信息与编码理论、电路理论、信号处理与通信、模拟与数字信号处理。主要研究方向包括信号处理、人工智能算法、计算机辅助工程教育以及高等教育教学法。
Dr. Katarzyna Moscinska, foreign teacher for Analog and Digital Signal Processing, professor and the vice dean of teaching affairs of the Faculty of Automatic Control, Electronics, and Computer Science of the Silesian University of Technology. Prof. Moscinska has extensive teaching experience. She teachers courses including Neural Networks, Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering, Fundamentals of Signal Processing, Digital Signal Processing, Computer Analysis of Electronic Circuits, Information and Coding Theory, Circuit Theory, Signal Processing and Communication, and Analog and Digital Signal Processing. Her scientific interests include signal processing, artificial intelligence algorithms, computer-aided engineering education and pedagogy in higher education.
Mourad Hakmaoui,博士,担任《模拟与数字信号处理》课程的外方实验教师。Mourad博士精通Python、Java、C++等多种编程语言,熟悉数据结构与算法、软件开发流程及数学建模,致力于推动计算机科学教育与应用研究的结合。
Dr.Mourad Hakmaoui, foreign laboratory teacher for Analog and Digital Signal Processing. Dr. Mourad is proficient in various programming languages such as Python, Java, and C++, with expertise in data structures and algorithms, software development processes, and mathematical modeling and is committed to promoting the integration of computer science education with applied research.
谈爱玲,博士,担任《模拟与数字信号处理》课程的中方共课教师。现就职于燕山大学信息科学与工程学院,光电子工程系副教授。主要讲授信号与系统,模拟与数字信号处理、模拟电子技术、电子设备与电路等课程。主要研究方向包括光谱分析技术及应用,目标检测、深度学习等。
Dr. Tan Ailing, Chinese teacher for the lecture session of Analog and Digital Signal Processing, associate professor from the School of Information Science & Engineering of Yanshan University. She offers courses including Signals and Systems, Analog and Digital Signal Processing, Analog Electronic Technology, and Electronic Devices and Circuits. Her primary research interests include spectroscopic analysis techniques and applications, object detection, and deep learning.
牛力勇,博士,担任《模拟与数字信号处理》实验的中方共课教师。现就职于燕山大学电气工程学院,电子实验中心实验师。主要研究方向表面等离子激元,光纤传感等。
Dr. Niu Liyong, Chinese teacher for the lab session of Analog and Digital Signal Processing from School of Electrical Engineering of Yanshan University. His main research focuses on surface plasmon polaritons, optical fiber sensing and related fields.
三、团队合作
Teamwork
在教学工作正式开始之前,双方教师依据中外联合课程规范化建设要求,首先通过电子邮件就课程教学安排进行了积极且高效的前期沟通。待Katarzyna教授与Mourad博士分别抵达燕山大学后,学院专门组织了联合教学讨论会。双方基于去年该课程的教学反馈,对理论与实验教学内容作了进一步优化,明确了各自的教学重点,确定了相应内容的课时分配、授课方式以及课程的整体考核办法。通过此次面对面交流,双方在教学安排上达成一致,为后续教学工作的顺利开展奠定了基础。
Prior to the start of the course, Chinese and foreign faculty members conducted active and efficient preliminary communication via email regarding the course arrangement based on the Sino-foreign joint course standardization project. After Prof. Katarzyna and Dr. Mourad arrived at Yanshan University, the college specially organized a joint teaching discussion meeting. Based on the teaching feedback from last year's course, both sides further optimized the theoretical and experimental contents, clarified the respective teaching priorities, and determined the allocation of class hours, teaching methods, and the overall assessment methods. Through this face-to-face communication, the two sides reached a consensus on the teaching arrangement, laying a foundation for the smooth implementation of subsequent teaching activities.
具体而言,理论课程的教学由Katarzyna教授承担。她在授课中英语语言表达准确、内容组织有序,讲解深入浅出,富有条理。为帮助学生更好地掌握知识,她每节课均采用PPT演示与板书相结合的方式,将重点与难点内容在黑板上逐一呈现,并尽可能多地举例子加以讲解,逐步分解复杂问题,有效帮助学生理解关键知识点。此外,Katarzyna教授注重课堂互动,积极鼓励学生发言并参与讨论,营造良好的学习氛围。图1为Katarzyna教授授课时的场景。图2为Katarzyna教授奖励学习特别认真的同学时的场景。
Specifically, Prof. Katarzyna was responsible for delivering the theoretical knowledge of the course. Her teaching was characterized by accurate English expression and well-organized content, and explained profound theories in simple and well-structured manner. To facilitate student learning, she combined slides with blackboard writing in each lecture to highlight key points and difficult topics, explained with as many examples as possible and gradually broke down complicated problems, effectively helping students understand the key knowledge points. Furthermore, Prof. Katarzyna emphasized classroom interaction, actively encouraging students to voice their opinions and participate in discussions, fostering a positive and engaging learning atmosphere.Figure 1 shows a photo of Prof. Katarzyna teaching during a lecture. Figure 2 captures the scene when Prof. Katarzyna was rewarding hardworking students.
中方共课谈爱玲老师负责协助理论课程的教学管理。她密切关注学生的出勤与听课状态,课前及时将PPT资料上传至班级课程群,并在课后适时梳理重点难点内容,发布至群内以供复习参考。同时,她还承担理论部分的课后答疑工作,为学生提供理论课程的学习支持。
Dr. Tan Ailing was responsible for assisting with the theoretical course. She paid close attention to student’ attendance and engagement during lectures. She promptly uploaded the PowerPoint materials to the class group before each lecture and distributed summaries of the key and challenging concepts to students for review after class. Additionally, she undertook the after-class Q&A work and provided students with learning support for the course.
在理论课程教学阶段,课程团队于第三周和第四周分别组织了两次课堂测验。中外教师提前协商,明确了每次测验所涵盖的知识范围、题型结构、题目数量以及考试时长与形式。两次测验均通过“雨课堂”平台统一实施。中方协助教师谈爱玲提前在系统中完成测试设置与发布工作。测验时间为20分钟,期间两位教师共同维持考场秩序,确保测验过程顺利进行。测验结束后,他们及时对学生的作答情况与成绩分布进行联合分析,通过数据反馈评估学生对知识点的掌握程度,为后续教学调整提供有效依据。图3为两次雨课堂随堂测验。
During the lectures phase, the course team conducted two in-class quizzes in the third and fourth weeks respectively. The foreign and Chinese teachers coordinated in advance to define the knowledge scope, question types and number, duration, and format for each quiz. Both quizzes were performed through the teaching platform "Rain Classroom". The teacher completed the test setting and published it ahead on the platform. Each quiz lasted 20 minutes, during which both teachers supervised the quizzes to ensure they proceeded smoothly. After the quizzes, they promptly conducted a joint analysis of student score distributions. This data-driven feedback helped evaluate the students' mastery of the knowledge and provide an effective basis for subsequent teaching adjustments. Figure 3 shows the data distribution of the two in-class quizzes.

图1 Katarzyna教授授课场景
Figure 1. Photo of professor Katarzyna teaching

图2 Katarzyna教授奖励学习特别勤奋的同学
Figure 2. Photo of professor Katarzyna awarding diligent students
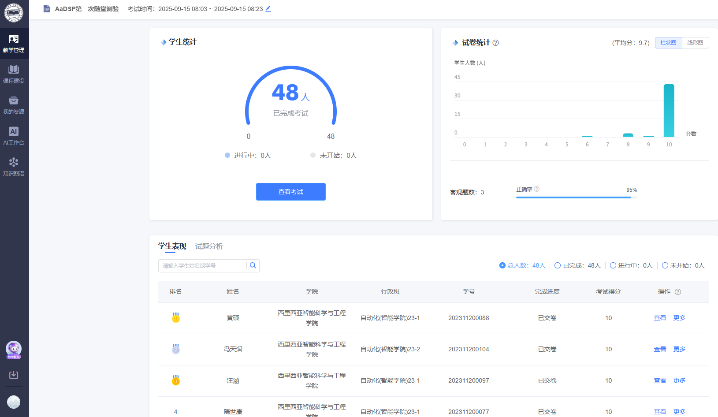
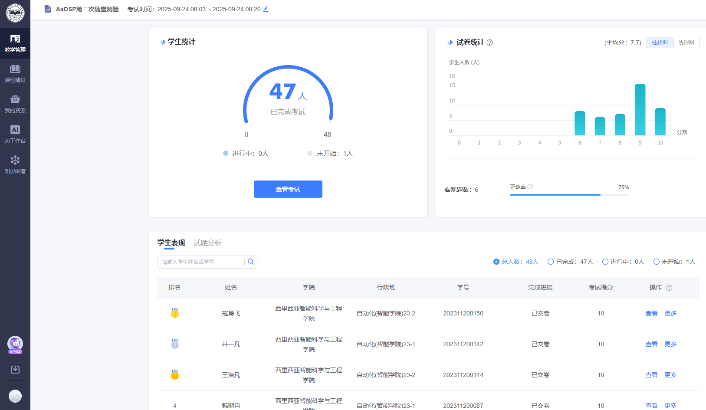
图3 雨课堂平台课堂测验
Figure 3: In-Class quizzes on the Rain Classroom platform

图4 理论课大合影
Figure 4. Group photo of lecture class
理论教学基础上,实验环节由Mourad博士主导,牛力勇与王荣彦老师协同指导。三位教师共同引导学生完成与课程相关的实验任务,帮助学生进一步巩固理论知识,并理解其在工程实践中的具体应用,有效提升了学生的综合能力。图5是上实验课的照片。
Based on the lecture teaching, the laboratory teaching was led by Dr. Mourad, with collaboration from the Chinese lab teachers Niu Liyong and Wang Rongyan. Three teachers jointly supervised students in completing course-related laboratory tasks, helped them further consolidate theoretical knowledge and understand its specific applications in engineering practice, effectively enhancing students' comprehensive abilities.Figure 5 shows a photo from the lab class.

图5 实验课
Figure 5. Photo of lab class
四、课程内容
Course Information
《模拟与数字信号处理》课程是解决各式各样复杂变化的信号和系统背后许多共性问题的课程。它建立了一套信号及系统分析的理论体系,内容丰富,涉及信号分析、系统分析和基于信号的系统响应分析等方面。 研究采用时域法和基于变换的变换域法,分别针对连续时间和离散时间信号与系统开展研究。该课程既具有很强的理论性与逻辑性, 同时更是一门具有物理意义和工程应用背景的课程。整个课程分为两个主要部分:理论课程和实验课程。理论课程共计12次课,涵盖了信号在时域和频域的表示、傅里叶级数、傅里叶变换、模拟调制系统、从模拟信号到离散时间信号的转换(采样定理)、离散信号的特性、离散系统的描述方法、Z变换、离散傅里叶变换(DFT)等内容,帮助学生建立起系统的理论框架。实验环节安排6次课,依托LabVIEW图形化编程平台,开展模拟与数字信号的仿真实践。通过实验,学生能够深化对理论知识的理解与应用,提升工程实践能力,掌握信号分析、测量及信号处理系统设计等核心技能,从而有效培养解决实际工程问题的综合素养。
Analog and Digital Signal Processing is a course designed to address common challenges underlying diverse and complex signals and systems. It establishes a theoretical framework for signal and system analysis, covering a broad range of topics including signal analysis, system analysis, and system response analysis based on signals. The course employs both time-domain methods and transform-domain methods to study continuous-time and discrete-time signals and systems, respectively. It is characterized by both strong theoretical rigor and logical structure and physical significance and engineering applications. The course includes lectures and laboratory sessions. The lecture consists of 12 classes, covering topics such as signal representation in time and frequency domains, Fourier series and Fourier transform, analog modulation systems, conversion from analog to discrete-time signals (sampling theorem), discrete signals, description methods for discrete systems, Z-transform and discrete Fourier transform. Those topics help students build a systematic theoretical foundation.The lab session includes 6 classes in which the LabVIEW graphical programming platform is used to simulate analog and digital signals. Through these experiments, students can deepen their understanding and application of theoretical knowledge, enhance their engineering practical skills, and master core competencies such as signal analysis, measurement, and signal processing system design, which effectively cultivates their comprehensive ability to solve real-world engineering problems.
理论课程内容:
Lectures contents:
Lecture 1 - Introduction
本节作为导论,首先介绍信号处理的广泛应用,模拟/数字、连续/离散时间信号的概念与各种分类方式;然后复习拉普拉斯变换与复数等分析线性系统的关键数学基础,并引入在时域和频域中描述信号的方法;最后概述课程涵盖的从模拟到数字信号处理的核心知识体系,并明确考核方式。
Lecture 1 serves as an introduction. It begins with an overview of overview of the broad applications of signal processing and introduces concepts and classifications of analog/digital and continuous/discrete-time signals. Then the key mathematical foundations for analyzing linear systems, including the Laplace transform and complex numbers are reviewed, also methods for describing signals in both the time and frequency domains were introduced. Finally, the core knowledge system covers in the course from analog to digital signal processing are outlined, and the assessment methods are clarified.
Lecture 2 -Frequency representation of periodic signals
本节介绍周期信号的频域表示方法-傅里叶级数。从分析非正弦周期信号通过线性系统时所面临的困难出发,引出将复杂信号分解为一系列正弦谐波成分的思想。通过引入正交函数集,详细推导三角形式的傅里叶级数,并给出计算各谐波幅度与相位的具体公式。介绍如何将正弦与余弦分量合成为单一余弦波,从而得到幅度-相位表示形式,并通过方波的分解实例展示了傅里叶级数如何用有限个谐波来逼近任意周期信号。
Lecture 2 introduces the frequency domain representation of periodic signals: the Fourier series. Beginning with the challenges of analyzing non-sinusoidal periodic signals passing through linear systems, the concept of decomposing complex signals into a series of sinusoidal harmonic components is introduced. By introducing orthogonal function sets, the trigonometric form of the Fourier series is derived in detail, along with specific formulas for calculating the amplitude and phase of each harmonic component. How to synthesize sine and cosine components into a single cosine wave is explained, How Fourier series can approximate periodic signals using a finite number of harmonics is demonstrated through an example of decomposing a square wave.
Lecture 3 -Frequency representation of periodic signals – cont.
本节介绍指数形式傅里叶级数及其频谱表示,从三角傅里叶级数形式过渡到指数形式,定义了复傅里叶系数及其与三角系数的关系,介绍如何用幅度谱和相位谱来直观描述周期信号的频率构成。通过锯齿波实例讲解频谱的计算、分析与信号重建过程。介绍指数傅里叶级数的关键性质(如线性、时移、微分积分),信号对称性对频谱的影响和吉布斯现象。
Lecture 3 introduces the exponential form of the Fourier series and its spectral representation. Beginning with the transition from the trigonometric Fourier series to the exponential form, the complex Fourier coefficients and their relationship to the trigonometric coefficients are introduced. How to intuitively describe the frequency composition of periodic signals using magnitude spectra and phase spectra is explained. Through a sawtooth wave example, the process of calculating and analyzing spectra as well as signal reconstruction is demonstrated. Key properties of the exponential Fourier series such as linearity, time-shifting, differentiation, and integration are introduced. The impact of signal symmetry on the frequency spectrum and the Gibbs phenomenon are also explained.
Lecture 4 -Signals and systems Fourier transform
本节将频域分析从周期信号拓展至非周期信号,建立信号通过线性系统的频域分析框架。首先介绍如何利用傅里叶级数分析周期信号通过线性系统,然后引出适用于非周期信号的傅里叶变换正变换与逆变换的公式,并介绍其作为频谱密度函数的物理意义。列举指数信号、门函数、冲激函数及正余弦函数等关键信号的傅里叶变换,并介绍其一系列重要性质(如线性、时移、频移、卷积等)。最后介绍系统输出的频域计算方法,并在此基础上介绍信号无失真传输的条件,引入理想低通滤波器的概念和其物理不可实现性。
Lecture 4 extends frequency domain analysis from periodic to aperiodic signals and establishes a framework for analyzing signals passing through linear systems in the frequency domain. How to analyze periodic signals passing through linear systems using Fourier series is first explained, then the forward and inverse Fourier transform formulas applicable to aperiodic signals are introduced, along with the physical interpretation. The Fourier transforms of fundamental signals such as exponential signals, gate functions, impulse functions, and sinusoidal signals were introduced, followed by a series of important properties including linearity, time shifting, frequency shifting, and convolution. The frequency-domain analysis methods for system output is introduced, the conditions for distortion-free signal transmission, and the concept of the ideal low-pass filter along with its physical unrealizability is explained.
Lecture 5 -Amplitude modulation
本节介绍幅度调制(AM)的原理与实现。首先介绍调制的基本概念,标准幅度调制的含义,通过数学公式和频谱图分析其时域波形与频域结构(载波和上下边带),并重点介绍调制指数的概念,简要介绍AM信号的生成方法和包络检波和同步解调两种demodulation技术。介绍载波抑制的双边带调制(DSB-SC)和单边带调制(SSB),分析其频谱特点、生成方法以及更高的功率效率,最后从频谱搬移的角度阐述幅度调制的本质。
Lecture 5 introduces the principles and implementation of Amplitude Modulation (AM). The basic concept of modulation and the definition of standard amplitude modulation are first introduced, its time-domain waveform and frequency-domain structure (carrier and upper/lower sidebands) through mathematical formulas and spectral diagrams are analyzed. The concept of modulation index is emphasized. The AM signals generation and two demodulation techniques of envelope detection and synchronous demodulation are briefly covered. Carrier-suppressed Double-Sideband Modulation (DSB-SC) and Single-Sideband Modulation (SSB) are introduced, their spectral characteristics, generation methods, and higher power efficiency are analyzed. The essential nature of amplitude modulation is finally explained from the perspective of frequency spectrum shifting.
Lecture 6 -Frequency modulation
本节介绍角度调制,包括频率调制(FM)和相位调制(PM)的原理、分析与实现。从定义广义正弦信号及其瞬时频率与相位出发,讲述频率调制(FM)和相位调制(PM)在数学上的区别与内在联系。重点介绍调制指数β的概念,进而推导出估算带宽的卡森公式,并通过举例说明如何进行计算。
Lecture 6 introduces angle modulation, covering the principles, analysis, and implementation of both Frequency Modulation (FM) and Phase Modulation (PM). The definition of a generalized sinusoidal signal and its instantaneous frequency and phase is introduced, the mathematical distinctions and intrinsic relationships between FM and PM are explained. The concept of modulation index (β) was emphasized, followed by the derivation of Carson's rule for estimating bandwidth. Illustrative examples are provided to demonstrate practical calculations.
Lecture 7 -Practical systems - restrictions Impulse modulation
本节介绍如何将连续的模拟信号转换为离散的数字信号。介绍理想低通滤波器(ILPF) 的阶跃和冲激响应特性,并基于Paley-Wiener条件讲述此类理想系统在物理上是不可实现的,引出对实际低通滤波器的简要介绍。数学推导香农采样定理,通过多个例题的讲解,让学生进一步理解和掌握采样定理,消除抗混叠现象的采样条件;简要介绍采样后量化过程。
Lecture 7 explains the conversion of continuous analog signals into discrete digital signals. The step and impulse response characteristics of the Ideal Low-Pass Filter (ILPF) are analyzed and based on the Paley-Wiener criterion, why such ideal systems were physically unrealizable is explained, leading to a brief introduction to practical low-pass filters. The Shannon Sampling Theorem is mathematically derived, and through multiple example, students are guided to further understand and master the theorem, including the sampling conditions required to prevent aliasing. The quantization process following sampling is briefly introduced.
Lecture 8 -Discrete signals
本节介绍离散时间信号与系统的基本概念和分析方法。介绍离散信号的定义、基本变换操作,如镜像、移位和缩放,以及将任意序列分解为偶分量与奇分量的方法。介绍几种基本且重要的离散序列:单位采样序列、单位阶跃序列、指数序列和正弦序列。介绍离散正弦信号的频率特性。介绍线性时不变系统和单位采样响应h(n)的概念。推导求解离散系统输出的卷积和计算公式。通过离散系统微分方程的表达式定义IIR和FIR两种系统;最后,简要介绍系统的串联和并列方式以及系统的稳定性与因果性的判别条件。
Lecture 8 introduces the fundamental concepts and analytical methods of discrete-time signals and systems. The definition of discrete signals and basic operations such as mirroring, shifting, and scaling, as well as the decomposition of any sequences into even and odd components are introduced. Several essential discrete sequences are introduced: the unit sample sequence, unit step sequence, exponential sequence, and sinusoidal sequence. The frequency characteristics of discrete sinusoidal signals are also explained. The linear time-invariant (LTI) systems and the concept of the unit sample response h(n) are also covered. The convolution sum formula for computing the output of discrete systems is derived. Two types of systems—IIR and FIR were defined. Finally, Series and parallel configurations of systems, along with criteria for determining system stability and causality are briefly introduced.
Lecture 9 -Discrete signals and systems in time and frequency domain
本节介绍离散时间系统在时域与频域中的表示与分析方法。介绍递归系统IIR和非递归系统FIR的判别方法和主要优缺点。介绍如何使用延迟器、乘法器和加法器这些基本模块来构建离散系统的模拟图,具体举例讲解如何根据差分方程绘制离散系统的模拟图。介绍离散时间信号的傅里叶变换定义和存在条件,介绍离散系统频率响应H(ejω)的概念和物理意义。通过实例计算和讨论频率响应的幅度谱和相位谱特性,并总结离散时间傅里叶变换的一系列重要性质,包括线性、周期性、时移、卷积特性等。
Lecture 9 introduces the representation and analysis methods of discrete-time systems in both the time and frequency domains. How to distinguish IIR and FIR systems, along with their main advantages and disadvantages were explained. How to construct block diagrams of discrete systems using basic components such as delays, multipliers, and adders are introduced. Specific examples are given to illustrate how to draw system block diagrams based on given difference equations. The definition and existence conditions of the Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT) are introduced, followed by the concept and physical interpretation of the discrete system frequency response H(ejω). The magnitude and phase characteristics of the frequency response are calculated and discussed by giving examples. Finally, key properties of the DTFT including linearity, periodicity, time shifting, and the convolution property are summarized.
Lecture 10 -Z transform Discrete systems
本节介绍Z变换及其在离散时间系统分析与设计中的应用。介绍Z变换的定义和收敛域,介绍不同序列(有限长、右边、左边、双边序列)收敛域的不同形式。介绍了离散系统系统单位脉冲响应的Z变换即系统函数H(z)的定义,讲解如何将系统的线性常系数差分方程通过Z变换推导出系统函数H(z)的表达式。介绍直接I型 和直接II型两种结构表示的系统框图。介绍系统的零点和极点概念。
Lecture 10 introduces the Z-transform and its applications in the analysis and design of discrete-time systems. The definition of the Z-transform and the region of convergence (ROC) are introduced, the different forms of ROC for various sequence types of finite-length, right-sided, left-sided, and two-sided sequences are analyzed. The system function H(z) is introduced. How to derive the expression for H(z) by applying the Z-transform to the linear constant-coefficient difference equation of the system is explained. Two block diagrams of direct form I and direct form II are introduced. Finally, the concepts of system zeros and poles are introduced.
Lecture 11 - Pole – zero diagram
本节介绍如何利用系统函数的零极点图来分析离散时间系统的特性。举例讲解通过系统函数H(z)的有理分式分解为因式乘积来确定系统极点和零点在z平面上的位置。介绍递归(IIR)系统 和非递归(FIR)系统的零极点分布。介绍零极点位置与系统频率响应之间的联系。
Lecture 11 explains how to analyze the characteristics of discrete-time systems using the pole-zero plot of the system function. How to determine the locations of poles and zeros in the z-plane by decomposing the rational fraction form of the system function H(z) into a product of factors is demonstrated by giving examples. The pole-zero distributions of IIR and FIR systems are introduced. It also explains The relationship between pole-zero locations and the system's frequency response is explained.
Lecture 12 -Discrete Fourier Transform. Fast Fourier Transform
本节介绍离散傅里叶变换(DFT)及快速傅里叶变换(FFT)。介绍DFT的定义,时域采样与频域采样之间的关系;介绍DFT的卷积特性,通过多个具体实例(如不同长度的正弦信号和多项式信号)讲解DFT的计算与频谱分析。简要介绍快速傅里叶变换(FFT) 的基本概念。
Lecture 12 introduces the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) and the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). The definition of the DFT and the relationship between time-domain sampling and frequency-domain sampling are introduced. The convolution property of the DFT is explained, and examples such as sinusoidal signals and polynomial signals of varying lengths are given to illustrate DFT computation and spectral analysis. The fundamental concept of the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is briefly introduced.
实验课程内容:
Laboratory contents
Tutorial 1- LabVIEW使用及谐波分析
1.通过分析和创建简单的程序框图来学习Labview图形化编程环境。在修改程序过程中熟悉控件和显示属性,学习波形查看和数据读取,掌握利用Labview编程环境学习信号处理过程的基本能力。
2.练习周期函数的傅里叶级数系数展开方法.利用公式对目标信号RMS,MEAN,ak,bk,Ck等相应数值进行求解,并使用Labview里的相关程序进行验证,掌握傅里叶级数系数与信号特征量关系。
Tutorial 1 - LabVIEW Usage and Harmonic Analysis
1. Learn the LabVIEW graphical programming environment by analyzing and creating simple block diagrams. Familiarize yourself with the properties of controls and indicators while modifying programs, practice waveform viewing and data reading, and master the fundamental skills of using the LabVIEW programming environment to study signal processing.
2. Practice the Fourier series coefficient expansion method for periodic functions. Use formulas to calculate relevant values such as the target signal's RMS, MEAN, ak, bk, and Ck, and verify these calculations using LabVIEW's built-in tools. Understand the relationship between Fourier series coefficients and signal characteristics.
Tutorial 2 -周期信号与线性系统
该练习的主要目标是观察通过线性电路传递的周期性信号。该练习包括四个任务:对周期性信号进行傅里叶级数分析;并通过模拟电路来观察和分析这些信号在通过不同滤波器时的行为,调整滤波器的参数决定了信号中哪些频率成分会被保留;通过调整滤波器的参数,可以实现对信号的微分(高通滤波)或积分(低通滤波)效果;观察不同参数对信号的影响,如信号的均方根(RMS)值、幅度谱和相位谱,从而加深对信号处理原理的理解。
Tutorial 2 - Periodic Signals and Linear Systems
The objective of this tutorial is to observe periodic signals transmitted through linear circuits. The exercise includes four tasks: performing Fourier series analysis on periodic signals; using simulated circuits to observe and analyze the behavior of these signals as they pass through different filters; adjusting filter parameters to determine which frequency components are preserved; achieving differentiation (high-pass filtering) or integration (low-pass filtering) effects by adjusting filter parameters; and observing the impact of different parameters on signal characteristics, such as RMS value, amplitude spectrum, and phase spectrum, to deepen the understanding of signal processing principles.
Tutorial 3 -傅立叶变换
通过用Labview程序显示各类特定函数及其频谱,学习连续傅里叶变换中函数与频谱关系,掌握绘制频谱方法。认识连续傅里叶变换中对偶性质,时间移动性质,积分(导数)之间的关系,时间标度性质。
Tutorial 3 - Fourier Transform
Learn the relationship between functions and their frequency spectra in continuous Fourier transforms by using LabVIEW programs to display various specific functions and their spectra. Master the method of plotting frequency spectra. Understand the duality property, time-shifting property, relationship between integration (differentiation), and time-scaling property in continuous Fourier transforms.
Tutorial 4 -信号调制与解调
练习的主要目的是让学生熟悉模拟调制系统的背景, 连续调制系统包括调幅和角度调制。具体练习包括基本的调幅(AM),抑制载波 (AM-SC),边带传输(SSB),了解幅度调制系统噪声抑制特性,掌握同步解调的基本性质。相位调制 (PM) 和频率调制 (FM),观察并绘制各种偏差值和不同调制信号的频谱。
Tutorial 4 - Signal Modulation and Demodulation
The objective of this tutorial is to familiarize students with the background of analog modulation systems. Continuous modulation systems include amplitude modulation and angle modulation. Specific exercises include basic amplitude modulation (AM), suppressed carrier modulation (AM-SC), and single-sideband transmission (SSB). Understand the noise suppression characteristics of amplitude modulation systems and master the basic properties of synchronous demodulation. Study phase modulation (PM) and frequency modulation (FM), and observe and plot the spectra for various deviation values and different modulation signals.
Tutorial 5 -信号采样及数字化
信号采样和数字化是数字信号处理的基础,它涉及将模拟信号转换成数字信号的过程。本练习研究采样,量化和信号重建过程,掌握奈奎斯特-香农采样定理,了解如何设置正确采样的参数,了解混叠现象,并能够识别影响数字化信号重建质量的参数。
Tutorial 5 - Signal Sampling and Digitization
Signal sampling and digitization form the foundation of digital signal processing, involving the conversion of analog signals into digital signals. This tutorial investigates the processes of sampling, quantization, and signal reconstruction. Master the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem, learn how to set parameters for correct sampling, understand aliasing phenomena, and identify parameters that affect the quality of digitized signal reconstruction.
Tutorial 6 - Z变换及DFT
学习常用信号的Z变换,掌握极点与响应特性,学习采用Z变换进行线性时不变系统的分析,通过Z变换的极点位置分析系统的稳定性,利用Z变换理解信号的采样和重构过程,特别是在奈奎斯特采样定理的应用中。学习DFT(数字傅里叶变换)基本性质和算法,了解由频域采样引起的混叠问题。由具体算例理解分辨率,零填充,信号的窗口等作用。
Tutorial 6 - Z-Transform and DFT
Learn the Z-transform of common signals and master the relationship between poles and response characteristics. Use the Z-transform to analyze linear time-invariant systems and assess system stability by analyzing pole locations. Apply the Z-transform to understand signal sampling and reconstruction processes, particularly in the context of the Nyquist sampling theorem. Study the basic properties and algorithms of the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) and understand aliasing issues caused by frequency domain sampling. Use specific examples to comprehend the roles of resolution, zero-padding, and signal windowing.
五、参考书籍和线上资源
Reference Textbooks and Online Resources
1. Lathi B.P.: Signal Processing and Linear Systems. Berkeley Cambridge, 1998.
2. Lyons R. G.: Understanding Digital Signal Processing. Addison-Wesley, 1997.
3. Oppenheim A.V., Willsky A.S., and Hamid S.: Signals and Systems. Pearson 1996.
4.管致中.信号与线性系统.高等教育出版社,2011年6月第5版.
5.郑君里,信号与系统,高等教育出版社,2011年3月第3版.
6.奥本海姆,刘树棠译,信号与系统(中文版),西安交通大学出版社,2006年5月第2版.
7.https://ocw.mit.edu/courses/mechanical-engineering/2-161-signal-processing-continuous-and-discrete-fall- 008/lecture-notes/
8. https://ocw.mit.edu/resources/res-6-007-signals-and systems-spring-2011/lecture-notes/
六、教学成果
Teaching Outcomes
依托西里西亚智能科学与工程学院的中外联合教学模式,《模拟与数字信号处理》课程在教学层面取得了显著成果。课程采用中外双方老师负责制和全英文授课,整合波兰西里西亚技术大学与中国燕山大学双方的教学资源,充分激发学生的学习热情。外方教师侧重于课堂理论和实验指导教学,中方教师则着力于课程组织管理及课后指导等协助和支持工作,形成了良好的教学互补机制,培养国际化工科人才。具体教学成效集中体现在以下几个方面:
掌握理论知识与实际技能:通过理论和实验教学,在知识层面,让学生掌握时域和频域中模拟信号与系统、离散信号与系统的相关概念,基本原理和分析方法;在技能层面,锻炼了学生应用信号处理的基本定理、 分析特定信号处理系统的特性和应用计算机仿真进行信号处理的能力。
提升国际化工程素养:通过多文化背景的师资配置与全英文互动教学模式,让学生掌握到相关的英文专业术语和词汇,帮助他们接触到更多的教学资源和文献,更好地了解国际学术前沿和发展趋势,并且提升学生的英语阅读、听说以及专业知识运用能力,使他们更具竞争力和国际视野。
培养工程性思维:通过理论与实验相结合的教学方式,帮助学生深入理解信号和系统基本原理和分析方法及其在实际工程中的应用,提高他们分析和解决实际问题的能力,培养具备扎实理论功底,又拥有工程性观点和思维的复合型人才。
提升多元化学习能力:通过充分调动学生在全英文课堂上主动学习,引导学生通过互联网展开启发式学习,自主探究与反思性学习,有效锻炼学生的多元化学习能力和创新意识。
综上所述,《模拟与数字信号处理》课程中外深度融合的教学机制,不仅强化了学生的专业知识与科研能力,更拓展了其国际化视野与创新能力,为学生未来的专业发展和国际交流打下了坚实的基础。
The Sino-foreign joint teaching model of the Silesian College of Intelligent Science and Engineering for the course "Analog and Digital Signal Processing" has achieved remarkable teaching outcomes. The course adopts a dual-responsibility of Chinese and foreign teachers and is conducted entirely in English, integrating teaching resources from both the Silesian University of Technology in Poland and Yanshan University, fully stimulating students' enthusiasm for learning. Foreign teachers focus on theoretical and laboratory guidance, while Chinese teachers are dedicated to assisting and supporting the organization and management of courses as well as after-class guidance, forming an effective complementary teaching mechanism to cultivate international engineering talents. The specific teaching outcomes are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Master theoretical knowledge and practical skills: Through lectures and lab teaching, students acquire relevant concepts, fundamental principles, and analytical methods of analog and discrete signals and systems in both time and frequency domains at the knowledge level. At the skill level, students have been trained to apply fundamental theorems of signal processing, analyze characteristics of specific signal processing systems, and utilize computer simulations for signal processing tasks.
Enhance international engineering competencies: Through a multicultural teaching team and a fully English-interactive teaching model, students have acquired relevant English professional terminology and vocabulary, gain exposure to a wider range of educational resources and literature, better understand international academic frontiers and development trends, improve their English reading, listening, speaking, and professional knowledge application skills, which makes them more competitive and broadens their global perspective.
Cultivate engineering thinking: Through a teaching approach that combines lectures with experiments, students have gained a deeper understanding of the fundamental principles and analytical methods of signals and systems, as well as their applications in practical engineering, thereby enhancing their ability to analyze and solve practical problems. In the end, They will develop solid theoretical foundations along with engineering perspectives and thinking.
Enhance diversified learning capabilities: By fully motivating students to actively engage in the fully English-speaking class and guiding them to conduct heuristic learning, independent inquiry, and reflective learning through the internet, the course has effectively enhanced students' diversified learning abilities and innovative thinking.
In summary, the integrated Sino-foreign teaching model of the "Analog and Digital Signal Processing" course has not only strengthened students' professional knowledge and research capabilities, but also broadened their global perspectives and innovative capacities, laying a solid foundation for their future professional development and international exchanges.
七、展望
Future Work
基于现有实践基础,西里西亚智能科学与工程学院的中外合作教学的未来发展将呈现更广阔而深入的图景。在《模拟与数字信号处理》课程建设方面,我们将进一步融合中外教育理念与方法,利用智能化技术实现中外师资协同教学与学生的个性化学习。在人才培养方面,《模拟与数字信号处理》不仅通过国际化课程内容拓宽视野,更将通过中外双导师制、国际项目式学习等多元路径,培养学生的跨文化沟通能力与创新能力,使学生成为真正具备国际竞争力的专业人才。同时,《模拟与数字信号处理》课程将通过建立教学质量监测反馈机制、学习成果评估标准等,持续优化合作教学模式,确保教育教学质量与人才培养成效的持续提升。
Based on the existing practical foundation, the Sino-foreign collaborative teaching development of the Silesian College of Intelligent Science and Engineering will present a broader and more profound prospects. In terms of developing the "Analog and Digital Signal Processing" course, we will further integrate Chinese and foreign educational philosophies and methods, leveraging intelligent technologies to facilitate collaborative teaching between Chinese and international faculty and enable personalized student learning.The course of "Analog and Digital Signal Processing" will not only broaden students' horizons through its international curriculum content but also foster their cross-cultural communication skills and innovative capabilities through diverse pathways such as the Sino-foreign dual-supervisor system and international project-based learning, enabling students to become truly internationally competitive professionals. Meanwhile, we will continuously optimize the collaborative teaching model by establishing mechanisms for monitoring teaching quality, feedback systems, and learning outcome assessment standards, to ensure sustained improvements in teaching quality and student learning outcomes.




